Create Machine configure NodeManager using WLST
This blog post is renovated with latest WebLogic 12.2.1 version execution output here. We have more generic reusable functions, three different functions each one has independent task. Where the pre condition for this is you must have a domain configured and admin server is running.
- create a machine and setup the Nodemanager
- delete machine from the domain
- show all machines in the domain
#==========================================================================
# FileName : createMachine.py
# Updated : 11/22/2015
# Description:
# This simple script will create multiple machines
# and also set the NodeManager properties
# use demo.properties file loadProperties command line argument expected
#
# You can add this function block to full domain
#==========================================================================
def createMachine(machineName, machineIP,nmPort=5556):
"""
This function takes three arguments machineName, machineIP, nmPort
The default nmPort is 5556 and nmType as Plain
"""
cd('/')
cmo.createUnixMachine(machineName)
cd('/Machines/'+machineName+'/NodeManager/'+machineName)
cmo.setNMType('Plain')
cmo.setListenAddress(machineIP)
cmo.setListenPort(nmPort)
cmo.setDebugEnabled(false)
def deleteMachine(machineName):
"""
This function takes machineName as argument
It will delete the Machine MBean from the Domain
"""
cd('/')
editService.getConfigurationManager().removeReferencesToBean(getMBean('/Machines/'+machineName))
cmo.destroyMachine(getMBean('/Machines/'+machineName))
def printMachineList():
"""
This function will display the machines configured on a domain
No arguments required
"""
cd('/')
redirect('/dev/null', toStdOut='false')
machineslist=ls('Machines',returnMap='true')
for m in machineslist: print m
stopRedirect()
def main():
"""
Here we can expect ConnectionException, WLSTException
and also BeanAlreadyExist for createMachine function
"""
connect(ADMINUSER,ADMINPASSWD, ADMINURL)
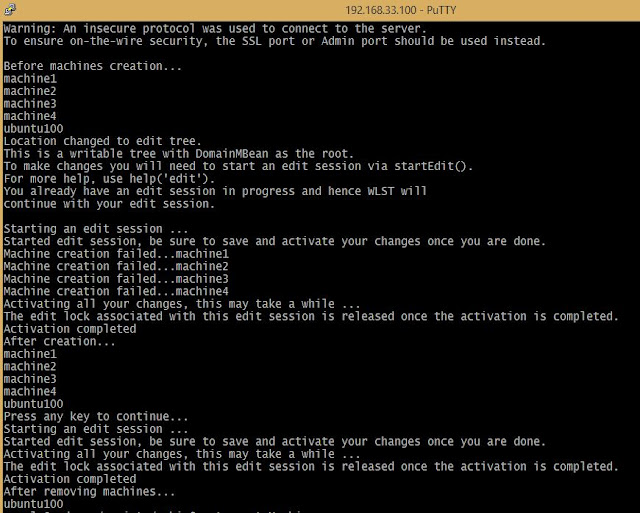
print "Before machines creation..."
printMachineList()
edit()
startEdit()
for i in range(1,5):
try:
createMachine('machine'+str(i), '192.168.33.'+str(100+i),5566)
except:
print 'Machine creation failed...'+'machine'+str(i)
activate()
print "After creation..."
printMachineList()
HitKey=raw_input('Press any key to continue...')
startEdit()
for i in range(1,5):
try:
deleteMachine('machine'+str(i))
except:
print 'Unable to remove machine...'
activate()
print "After removing machines..."
printMachineList()
main()
Excecution of the Machine configuration is as follows....
java weblogic.WLST -loadProperties demo.properties createMachine.py
 |
| create, delete and show machines in WebLogic 12.2.1 domain |
Double confirmation with Admin console
 |
| Machine in WebLogic Domain configured with WLST |
Start n Stop the Server using NodeManager by WLST
Manage the Server Life Cycle continues...
[2] Configure a NodeManager to start WebLogic Server instances (using console and command-line)
Start n Stop Server using NodeManager by WLST:
In the sun Solaris environment we need to change few nodemanager.properties to run the NodeManager. There are two kinds of Node Managers available
Java based Node manager
Script based Node manager
while connecting to nodemanager we have received an error as below:
Error encounter when the java native
bash-3.00$ tail -100f nodemanager.log
weblogic.nodemanager.common.ConfigException: Native version is enabled but node manager native library could not be loaded
at weblogic.nodemanager.server.NMServerConfig.initProcessControl(NMServerConfig.java:239)
at weblogic.nodemanager.server.NMServerConfig.(NMServerConfig.java:179)
at weblogic.nodemanager.server.NMServer.init(NMServer.java:177)
at weblogic.nodemanager.server.NMServer.(NMServer.java:142)
at weblogic.nodemanager.server.NMServer.main(NMServer.java:327)
at weblogic.NodeManager.main(NodeManager.java:31)
Caused by: java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: no nodemanager in java.library.path
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadLibrary(ClassLoader.java:1682)
at java.lang.Runtime.loadLibrary0(Runtime.java:822)
at java.lang.System.loadLibrary(System.java:993)
at weblogic.nodemanager.util.UnixProcessControl.(UnixProcessControl.java:16)
at weblogic.nodemanager.util.Platform.getProcessControl(Platform.java:108)
at weblogic.nodemanager.server.NMServerConfig.initProcessControl(NMServerConfig.java:237)
... 5 more
java weblogic.WLST startAdmin.py wcludomNM
connect('weblogic', 'weblogic', 't3://wlhost:7913')
nmEnroll('/home/wluser/domains/WLclsnm')
CLASSPATH to set for NodeManager:
export NM_HOME = $WL_HOME/common/nodemanager
CLASSPATH=/export/home/wladmin/wl813/bea/jdk142_04/jre/lib/rt.jar:/export/home/wladmin/wl813/bea/jdk142_04/lib/rt.jar:/export/home/wladmin/wl813/bea/patches/CR204958_810sp3_v1.jar:/export/home/wladmin/wl813/bea/weblogic81/server/lib/weblogic.jar
startNodeManager(verbose='true',NodeManagerHome='/home/wluser/bea/weblogic92/common/nodemanager')
To Check the log of nodemanager.log
tail -100f /home/wluser/bea/weblogic92/common/nodemanager/nodemanager.log
/home/wluser/bea/weblogic92/common/nodemanager/nodemanager.domains>
nmConnect('weblogic', 'weblogic', 'wlshostname','5556', 'WLclsnm', '/home/wluser/domains/WLclsnm')
prps = makePropertiesObject('weblogic.ListenPort=9013')
wls:/WLclsnm/serverConfig>
wls:/WLclsnm/serverConfig> nmStart('app01',props=prps)
Starting server app02 ...
Error Starting server app02: weblogic.nodemanager.NMException:
Exception while starting server 'app02': java.io.IOException: Server failed to start up. See server output log for more details.
prps = makePropertiesObject('weblogic.ListenPort=9013')
start('wlctr', 'Cluster')
nmStart('app02',props=prps)
Starting server AdminServer...
Server AdminServer started successfully
nmConnect('weblogic', 'weblogic', 'remotehostnameofmanagedserver' '5556','WLclsnm', '/home/wluser/domains/','plain')
Still workin progress to start the remotemanaged server by using wlst
(I am getting some errors when I tried ...will update this site Once it will done successfully if anybody is done plz post it as comment.)
Posted by Pani at 9:44 AM 1 comments:
Archana said...
Hi,
We are also facing the same issue. Not able to start managed servers using makepropertiesobject.
Did u get any solution.
Yes, Archana, We found the Solution as using PLAIN type for NodeManager is good to go.